-
[3dgs] open3d로 point cloud 시각화Machine Learning 2024. 7. 4. 11:34
https://www.open3d.org/docs/release/tutorial/geometry/surface_reconstruction.html
Surface reconstruction - Open3D 0.18.0 documentation
Previous Octree
www.open3d.org
https://www.open3d.org/docs/latest/tutorial/Basic/pointcloud.html#DBSCAN-clustering
Point Cloud — Open3D latest (664eff5) documentation
This tutorial demonstrates basic usage of a point cloud. Paint point cloud print("Paint chair") chair.paint_uniform_color([1, 0.706, 0]) o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([chair], zoom=0.7, front=[0.5439, -0.2333, -0.8060], lookat=[2.4615, 2.1331, 1.338],
www.open3d.org
ply파일은 point cloud 와 mesh를 저장할 수 있는 포맷이다. 여기선 point cloud를 시각화했다.
시각화하기전에 mesh가 포함된 파일인지 확인해봤는데, Point cloud만 존재함을 알 수 있었다.
"TriangleMesh with 98500 points and 0 triangles."
98500개의 points만 존재하고, mesh를 이루는 triangles는 전혀 없다.
# ply 포맷 내용 읽기 path = ' '# '/workspace/gaussian-splatting/output/5e870fa5-9/point_cloud/iteration_30000/point_cloud.ply' with open(path, 'rb') as file: for i in range(100): ply_content = file.readline() print(ply_content)ply파일 구조
더보기- Header
- ascii 또는 binary_ll binary_little_endian 그리고 binary_big_endian
- Vertex List
- Face List (lists of other elements)
ply format ascii 1.0 { ascii/binary, format version number } comment made by Greg Turk { comments keyword specified, like all lines } comment this file is a cube element vertex 8 { define "vertex" element, 8 of them in file } property float x { vertex contains float "x" coordinate } property float y { y coordinate is also a vertex property } property float z { z coordinate, too } element face 6 { there are 6 "face" elements in the file } property list uchar int vertex_index { "vertex_indices" is a list of ints } end_header { delimits the end of the header } 0 0 0 { start of vertex list } 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 4 0 1 2 3 { start of face list } 4 7 6 5 4 4 0 4 5 1 4 1 5 6 2 4 2 6 7 3 4 3 7 4 01. 원본 Point Cloud 시각화
13초 분량의 영상 촬영 -> ffmpeg로 프레임별 사진으로 변환 -> COLMAP을 통한 카메라 파라미터 및 point cloud 생성 -> 딥러닝 3D gaussian splatting 의 입력값으로 COLMAP의 결과물을 활용 -> 학습 및 추론으로 나온 결과물 중 ply 포맷의 3d point cloud 를 시각화했다.
import numpy as np import open3d as o3d if __name__ == "__main__": print("Load a ply point cloud, print it, and render it") input_path = '/workspace/gaussian-splatting/output/5e870fa5-9/point_cloud/iteration_30000/point_cloud.ply' pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(input_path) print(pcd) print(np.asarray(pcd.points)) o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd]) # xhost +local:docker
PyVista라이브러리로 시각화
pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(input_path) pcd_np = np.asarray(pcd.points) point_cloud = pv.PolyData(pcd_np) # visualization with open3d point_cloud.plot(eye_dome_lighting=True)
2. Down-Sampling
print("Downsampling the point cloud with a voxel of 0.05") downpcd = pcd.voxel_down_sample(voxel_size=0.05) print(np.asarray(downpcd)) o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([downpcd])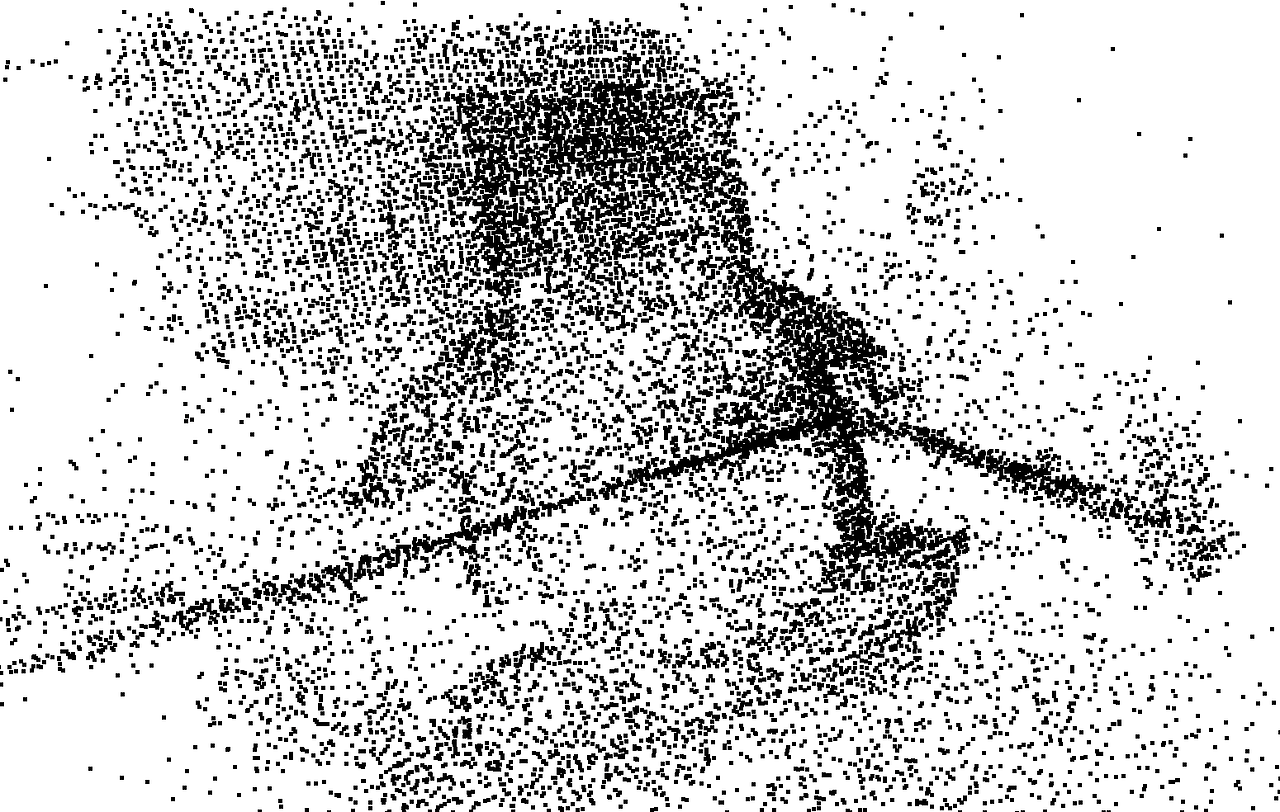
voxel_size의 단위는 m이고, 위 사진은 0.1m일 때의 point cloud(자율주행에서는 0.1, 0.2 많이 사용됨)

voxel_size = 0.05m 일 때
voxel 이라는 정육면체의 가상의 격자에 하나의 샘플만 들어가도록 샘플 수를 줄이는 것. voxel 사이즈를 정할 수 있고, 여기서는 0.05m이다. 참고
PointCloud with 98500 points 에서
PointCloud with 35469 points 수만큼 줄었다.
3. Vertex normal estimation
print("Recompute the normal of the downsampled point cloud") downpcd.estimate_normals(search_param=o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=0.1, max_nn=30)) o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([downpcd])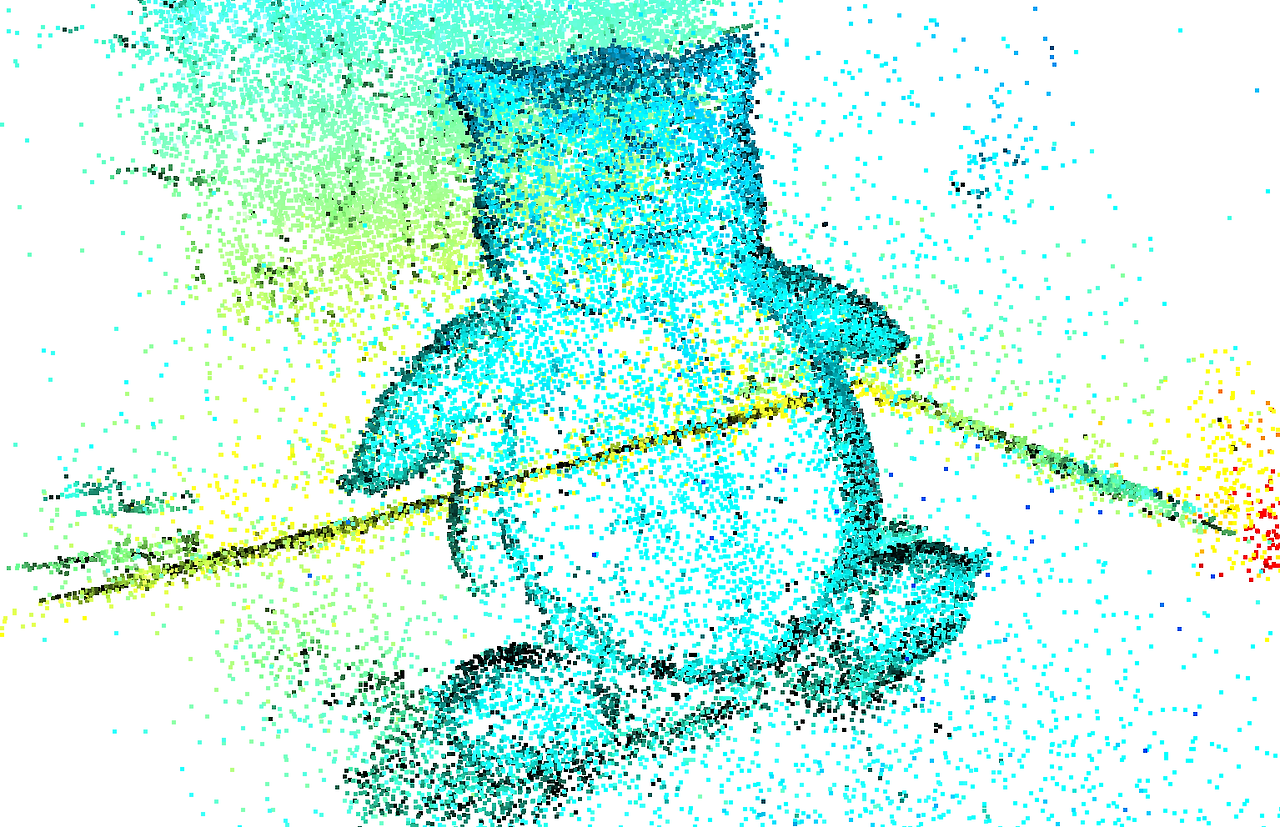
4. PCD to mesh (Alpha shapes)
point cloud를 mesh로 만드는 기법은 여러가지가 있다. Ball Pivoting, Poisson surface reconstruction 등, 그 중 Alpha shapes 방법을 사용해봤다.
alpha = 0.1 print(f"alpha={alpha:.3f}") mesh = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_from_point_cloud_alpha_shape(downpcd, alpha) mesh.compute_vertex_normals() o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh], mesh_show_back_face=True)
5. Point cloud clustering
import numpy as np import open3d as o3d import time import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import hdbscan print(o3d.__version__) input_path = '/workspace/gaussian-splatting/output/e025ca54-d/point_cloud/iteration_30000/point_cloud.ply' pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(input_path) voxel_down_pcd = pcd.voxel_down_sample(voxel_size=0.1) voxel_down_pcd.estimate_normals(search_param=o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=0.1, max_nn=30)) def display_inlier_outlier(cloud, ind): inlier_cloud = cloud.select_by_index(ind) outlier_cloud = cloud.select_by_index(ind, invert=True) print("Showing outliers (red) and inliers (gray): ") outlier_cloud.paint_uniform_color([1, 0, 0]) inlier_cloud.paint_uniform_color([0, 1, 0]) o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([inlier_cloud, outlier_cloud], zoom=0.3412, front=[0.4257, -0.2125, -0.8795], lookat=[2.6172, 2.0475, 1.532], up=[-0.0694, -0.9768, 0.2024]) # print("Statistical oulier removal") # cl, ind = voxel_down_pcd.remove_statistical_outlier(nb_neighbors=20, # std_ratio=2.0) # display_inlier_outlier(voxel_down_pcd, ind) print("Radius oulier removal") cl, ind = voxel_down_pcd.remove_radius_outlier(nb_points=40, radius=0.5) # display_inlier_outlier(voxel_down_pcd, ind) # Remove outliers pcd2 = inlier_cloud = voxel_down_pcd.select_by_index(ind) print(f"Number of points before removing outliers: {len(voxel_down_pcd.points)}") print(f"Number of points after removing outliers: {len(inlier_cloud.points)}") # Visualize the filtered point cloud pcd2.paint_uniform_color([0.5, 0.5, 0.5]) # o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([inlier_cloud]) t1 = time.time() plane_model, inliers = pcd2.segment_plane(distance_threshold=0.22, ransac_n=3, num_iterations=500) inlier_cloud = pcd2.select_by_index(inliers) outlier_cloud = pcd2.select_by_index(inliers, invert=True) inlier_cloud.paint_uniform_color([0.5, 0.5, 0.5]) outlier_cloud.paint_uniform_color([1, 0, 0]) t2 = time.time() print(f"Time to segment points using RANSAC {t2 - t1}") o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([inlier_cloud, outlier_cloud]) plane_model, road_inliers = pcd2.segment_plane(distance_threshold=0.22, ransac_n=3, num_iterations=500) pcd3 = pcd2.select_by_index(road_inliers, invert=True) # o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd3]) # CLUSTERING WITH HDBSCAN t3 = time.time() clusterer = hdbscan.HDBSCAN(min_cluster_size=30, gen_min_span_tree=True) clusterer.fit(np.array(pcd3.points)) labels = clusterer.labels_ max_label = labels.max() print(f'point cloud has {max_label + 1} clusters') colors = plt.get_cmap("tab20")(labels / max_label if max_label > 0 else 1) colors[labels < 0] = 0 pcd3.colors = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(colors[:, :3]) t4 = time.time() print(f'Time to cluster outliers using HDBSCAN {t4 - t3}') o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd3])
1~5의 과정을 다른 PCD에 적용해보았다. (아래 사진)

pcd 원본 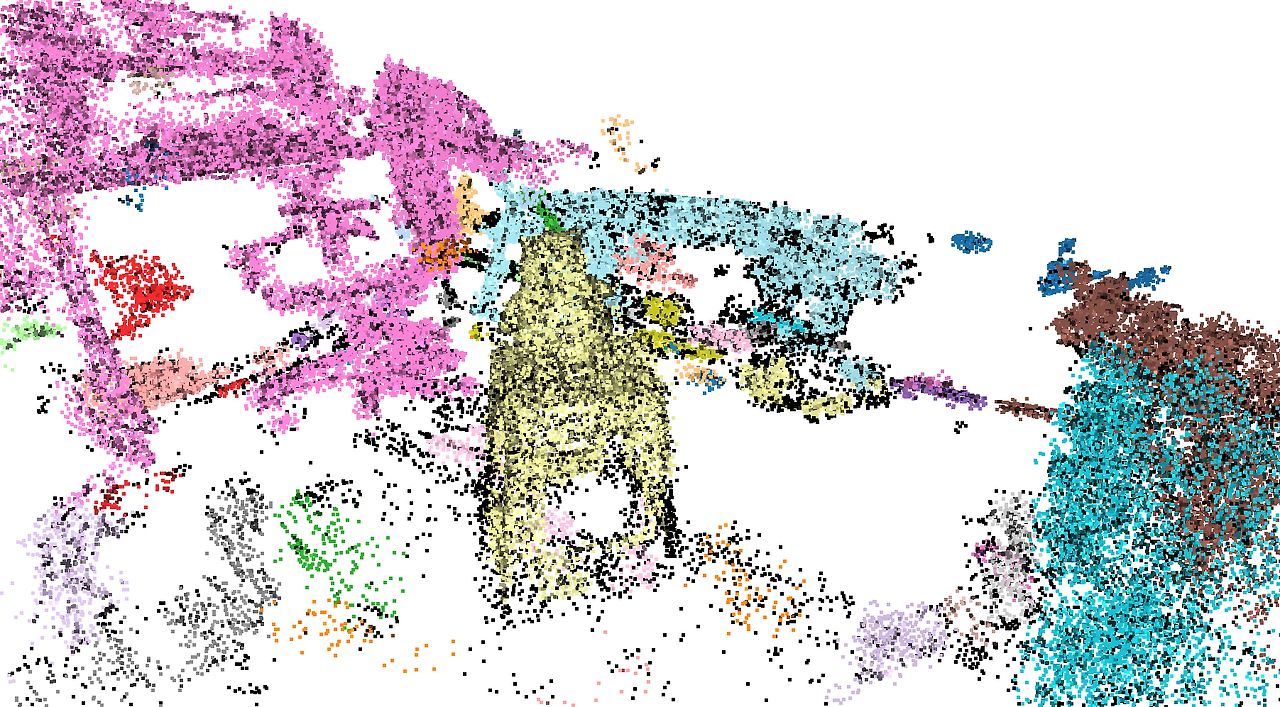
HDBSCAN 수행 후 'Machine Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
3D Gaussian splatting - SuGaR , dockerfile 작성 (0) 2024.08.18 Logistic regression, cross entropy (2) 2023.12.03 Batch Normalization (배치정규화) (2) 2023.12.03 [DL] Regularization (0) 2023.09.12 [DL] Gradient Descent Methods (0) 2023.09.12